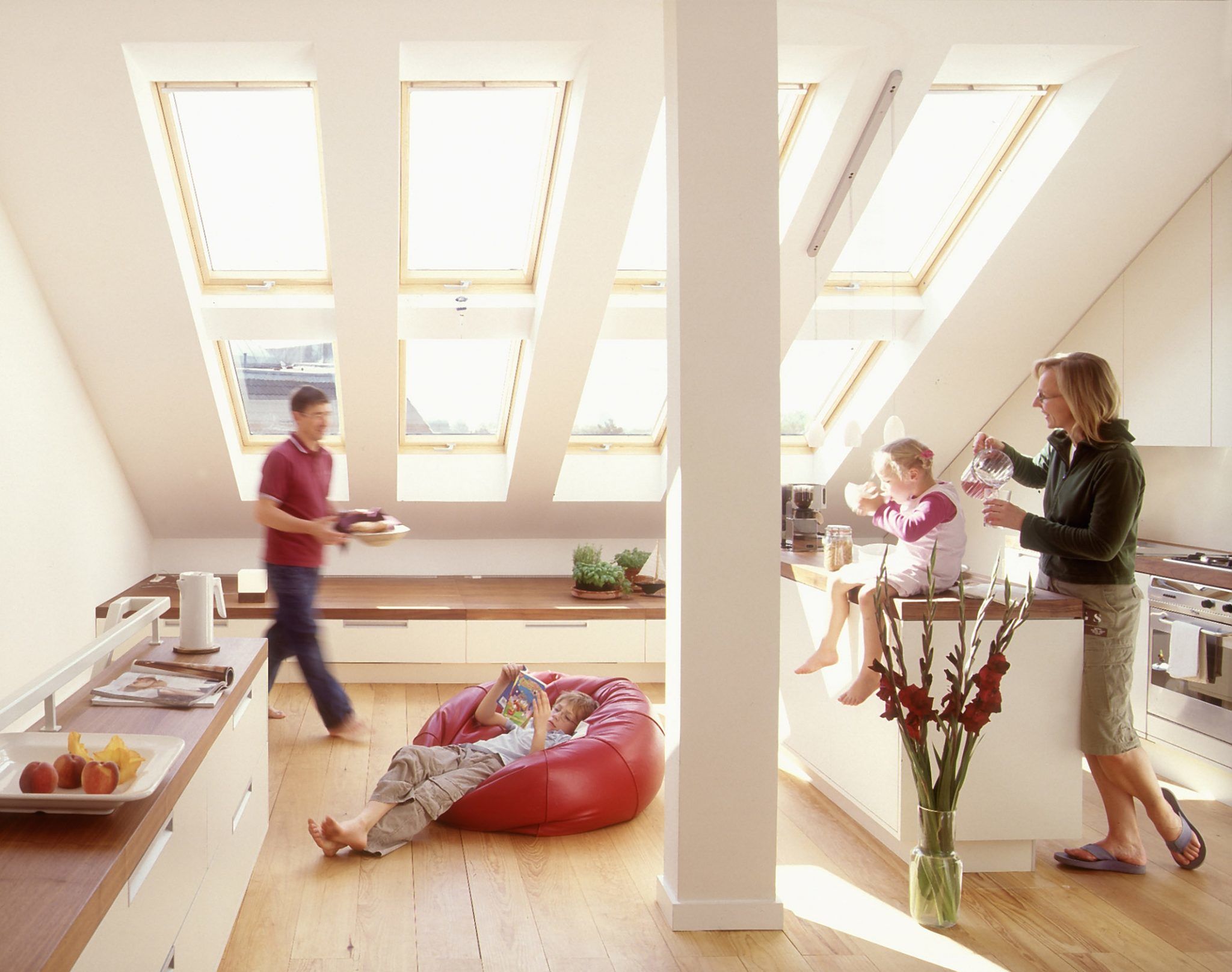
The view into the distance, the cool wind lifting the curtains, the sun’s rays flashing through the half-opened shutters in the morning – windows are filled with numerous positive images. The glass panes are a bridge between the inside and the outside and must fulfill a variety of functions: They provide light and ventilation and should create a comfortable living atmosphere by combining openness and privacy. Last but not least, of course, aesthetic and ecological demands are placed on their design, arrangement and execution. Oliver Williges from window manufacturer VELUX explained in an expert talk what needs to be considered in sustainable and energy-efficient window planning.
the essentials in brief
- When planning windows, it is essential to take into account the use of each room.
- In addition to a high level of thermal protection, the use of ecologically produced materials, a long service life of the entire window system, as well as low maintenance and care requirements are crucial.
- A corresponding minimum air exchange is important despite regular ventilation in order to transport moisture out and thus prevent mold growth.
How can windows support the natural biorhythm?
Bright apartments are popular on all sides. Few people feel comfortable in a gloomy, cool ground-floor apartment. There are even separate rules in the state building codes for daylighting interiors. According to them, the window area must usually be in a ratio of 1:8 to the floor area of the room. But of course, the lighting design can be further optimized by aligning the rooms for living, sleeping or working according to the incidence of daylight. If bedrooms are oriented to the east, you will be naturally awakened by sunlight in the morning and it will be easier for you to get out of bed. Workspaces, on the other hand, are best oriented to the north and, if possible, lit from above, because the diffuse sky light provides uniform illumination without glare. Floor plans that allow light to enter from at least two sides, following the natural course of the day, are particularly recommended. The comfort of the view should also not be underestimated as an important feel-good factor. Residents should be able to look out comfortably in any everyday situation – both standing and sitting. For this purpose, the bottom edge of the window should be about 90 cm.
What does an ecological window look like?
With regard to sustainability, aspects such as high thermal insulation of the frame and glass, the use of ecologically manufactured materials, a long service life of the entire window system, and low maintenance and care requirements are particularly decisive.

Source: VELUX Germany GmbH
Daylight
Daylight has a direct influence on physical and mental health, because the production of the hormones melatonin and cortisol depends on the intensity of sunlight. These in turn control the sleep-wake rhythm. That’s why it’s easier to get out of bed in the morning when the sun is shining!
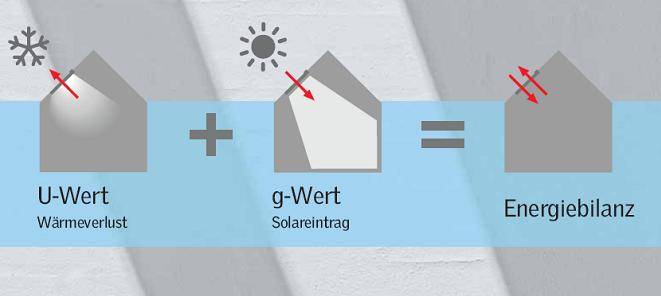
Good thermal insulation of the window and the ability to passively allow solar energy into the building are essential for the ecological rating. South-facing windows with triple glazing and an insulated frame, by collecting light and heat, can actually provide more energy gains than losses. The solar energy hitting the window, in the form of heat input, reduces the need for heating in the cold season and also helps to save electrical energy for lighting.
Solar gains
Information about how much of the incident solar heat reaches the interior of the room is provided by the so-called g-value. The smaller it is, the less solar heat penetrates into the room and vice versa.
Wooden frame profiles have more favorable ecological balance values than aluminum or PVC windows due to the lower energy expenditures in production. The good thermal insulation of the frame material brings additional advantages. Although wooden frames are not as weather resistant as aluminum or PVC windows, but if there is no particularly heavy use of the windows, they are definitely the better choice.
How to save energy with windows?
Thermal insulation value
The U-value is an important indicator of the thermal insulation capacity of building components or a window. It refers to the heat loss from the inside to the outside. The higher the U-value (heat transfer coefficient), the worse the thermal insulation of a body.
Windows have long had the reputation of being energy holes:
Heat losses in winter and excessive heat input from the sun in summer had a negative impact on the occupants’ sense of comfort as well as on the energy balance. However, thanks to modern coating technology and processing methods, heat loss through the glass has been greatly reduced. High thermal insulation of the frame and glass and a thermal insulation value of the window (U-value should be better than 0.9 W/m²K) are important factors for sustainably reducing the energy consumption of a house.
Source: VELUX Germany GmbH
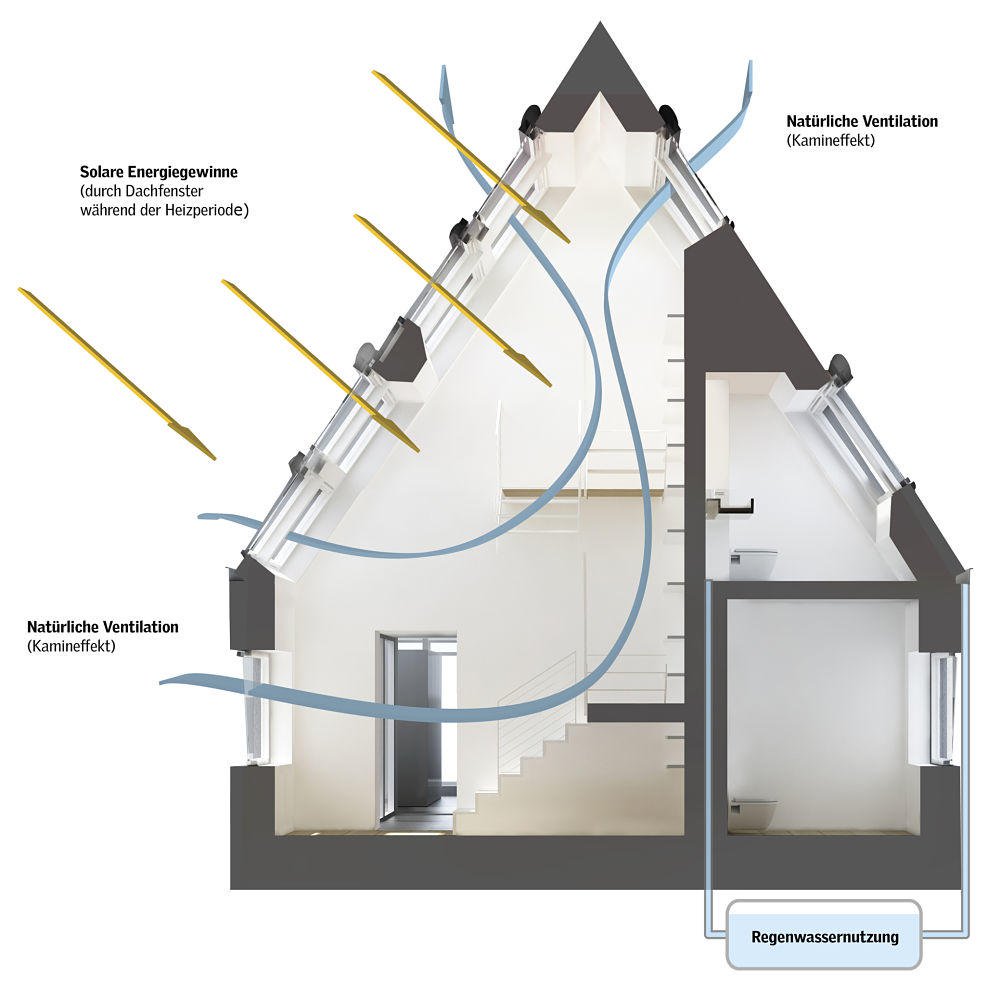
Through the interaction of the system components windows, roller shutters and sun protection, the heat input can be optimally regulated depending on the season and personal feeling. The replacement of old windows in combination with automatic control for sun protection and ventilation can thus make a significant contribution to energy optimization.
How do windows affect indoor air quality?
For some years now, the maxim for new construction projects has been to realize buildings that are almost airtight. In terms of low energy losses, this makes perfect sense, but unfortunately it is often forgotten that this also stops the exchange of air, which is to the detriment of healthy indoor air hygiene. Despite regular ventilation, a minimum air exchange is necessary to transport moisture, which is created by cooking, showering or washing, out of the living spaces. Otherwise, there is a risk of mold growth, which endangers both the building fabric and the health of the occupants. For this reason, the current Energy Saving Ordinance (EnEV) prescribes not only the airtight design of the building envelope, but also ensuring a minimum air exchange.
Source: VELUX Germany GmbH
Do you still have questions about window planning in general or about individual aspects such as thermal insulation, ventilation or the differences between individual window types? Our independent experts will be happy to advise you!
This article is based on an expert interview with Oliver Williges, employee of VELUX Deutschland GmbH
VELUX Deutschland GmbH, based in Hamburg, is a company of the international VELUX Group. The world’s largest manufacturer of roof windows is represented by more than 10,000 employees in around 40 countries. In Germany, the VELUX Group employs almost 1,000 people in production and sales. In addition to roof windows and sophisticated skylight solutions for pitched and flat roofs, the product range includes solar shading products, roller shutters and solar collectors, as well as accessory products for window installation. For more information, visit http://www.velux.de



